This post is intended not to make you an SEO expert but to provide you with enough knowledge to make your keywords visible to the search engines and to readers. On-page visible elements include headings, images, paragraph text, and other formatting elements. In this post, we will discuss the most important and how they can affect your SEO.
Heading Tags – On-Page Visible Elements
Heading Tags range from <h1> to <h6> and represent a cascading level of content similar to an outline. Headings are one of the primary ways search engine understand that your page is about. Therefore, it is important to include headings wherever naturally possible. Moreover, using headings allows readers to more easily scan your content. Content with just body text and no headings is less interesting, turns off many readers, and does not tell the search engines what is important.
When keywords are also used in Heading Tags, the search engine knows that it is important. For example, if you want to optimize for “Break-Even” and you are talking about fixes and variable costs rather than just use an <h2> tag with the word “Fixed”, using something like “Break-Even: Fixed Cost” will give the search engine a better idea of the context of the relationship between Break-Even and Fixed Cost.
If you hire a web developer, be aware that many web developers rely heavily on using Cascading Style Sheets to format a page. While using Cascading Style Sheets is not a bad thing, it is important to understand that they can be used in ways that do not help you with SEO. Web developers can often produce many pages that look like they have headers, but in fact, do not have any headers for the search engines to understand what are your most important keywords about your page. The process of using Cascading Style Sheets makes the web developer’s job easier, but as a business owner, you need to understand if their use of Cascading Style Sheets is at the expense of better SEO.
What I have discovered is that many web developers may say they also do SEO, they are, in fact, not very SEO savvy. When you select a web developer be sure that they are really competent in SEO. Many freelancing platforms like Upwork, the one I use, will administer tests to freelancers so you can see where your potential developer ranks in specific skills. For example, I can easily see that my web developer MissB, scored in the top 20% on her SEO test administered by Upwork.
Body Text Formatting – On-Page Visible Elements
The body text is where you communicate your message to your target market. This is where you make your argument that the reader should buy your product or service, or respond to your call to action. It is also where the search engines attempt to determine what the page is about by searching for keywords
Everything else like meta tags, your URL, title tags, description, and even headers are just proxy ways that search engines attempt to determine what a post is about. However, the body is why the reader is there in the first place, and therefore the use of keywords in your body text is weighted very highly by search engines.
First and foremost, make your pages easy to read for your audience. As we shared in How to Write a Sales Page there are Skimmers, Scanners, and Readers, and your text needs to be optimized for each. Here are the five best practices that will make sure that your copy will appeal to all three types of customers.
- Font size should vary and never be smaller than 16pt.
- Use short sentences that are no more than 40 to 80 characters long.
- Start a new paragraph after every three or four sentences.
- Use lots of lists, quotes, and tables to mix up the look.
- Use a new sub-headline for every two to three paragraphs.
When it comes to SEO, words that are bold and in italics not only bring attention to keywords for the readers but are used by search engines to learn what is important in your text. Therefore, you may want to bold or italicize your keywords to bring attention to them for the reader and for search engines, but don’t over go it.
Note: According to Matt Cutts of Google, <strong> and <b> for bold are two tags that both make the visible text bold. However, Google does not really treat the tag differently from an SEO perspective.
Images Tags – On-Page Visible Elements
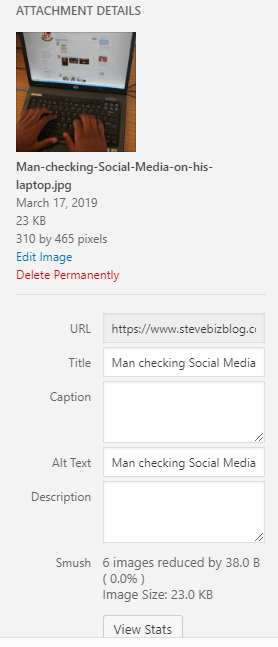
Images have a Title and an Alt Tag. Alt tags were originally designed to be the text that would appear if a user had their images turned off. The text in the alt tag was the text that would be displayed in the absence of the image. The alt tag text was also the text that would appear if you moused-over the image. However, nearly every user has the ability to display images these days, and few browsers display the alt tag’s text if your mouse over the image any more. So does that mean that the alt tag no longer has any value? To the contrary. Since search engines are currently not very good at searching image content, they use both the title tag and alt tag to understand what the image is about, and how it contributes to the overall understanding of the web page.
Consider a post that has a featured image of a guy sitting at a desk looking at a laptop, and the post is about using Social Media which is what you want the search engine to index your page for. You could enter “Man at Laptop” in the title as an alt tag but, it is far better to use “Man checking Social Media on his laptop”. Since the alt tag and title both contain the keyword “Social Media” which is the topic of your post and is one of the keywords you are trying to rank the page for, you give the search engines another clue to go on when indexing your page.
Internal Links
Internal links are links that go from one page on a domain to a different page on the same domain. You will want to include internal links to other pages whenever possible so long as the links appear natural because links pass page rankings, or what some call Link Juice, from one page to the other.
The Anchor Text is the text in your body text that is visible and highlighted for the user to show that it is a hypertext link that will take the reader to another page associated with the link. The words “Anchor Text” in the previous sentence is an example of anchor text.
The anchor text is yet another clue that search engines use to determine what the current page is about, and how it relates to other content on your site. Therefore, if possible, your anchor text is best if it is a keyword or at least a semantic equivalent.
For a long time, I always made the anchor text the title of the page I was linking to. While this practice is not bad, it would have often been a better SEO practice if I rewrote the text to include a keyword that I wanted to tell search engines about.
For example, if I had a page with a title of “Generational Behaviors and Attitudes” and I’m writing for a page I’m trying to rank for baby boomers, I could format the body text as follows:
“…in the article on Generational Behaviors and Attitudes we talk about baby boomers”
The anchor text in this example is the title of the target post “Generational Behaviors and Attitudes”. It is better from an SEO perspective to use “baby boomers” as the Anchor text in the body and not the post title. For example:
“…in the article on Generational Behaviors and Attitudes we talk about baby boomers”
In this case, the anchor text is the same as the keyword that I wanted to rank the current page for.
You absolutely want to avoid the all too common “click here for more information” anchor text, since “click here” is meaningless to the search engine.
Of course, whenever you are including an internal link, you want to make sure that the target page where the link takes the reader is also properly optimized.
Finally, when it comes to internal links, it is better to have a text link where the anchor text is a keyword that you are trying to optimize for than an image link. An image link is where the image can be clicked on to take the reader off the page. A common example is adding a “Buy now” button as a call to action on a page. If you use an image like that, be sure that the title and alt tags, as well as the URL communicate to the search engines what the link is about.
Expert Tips:
Getting some additional common keywords for your website listed on each page can be accomplished with what is known as a “link block”. A link block often appears at the bottom of a web page and acts as a site’s navigation to other parts of the website. Technically, link blocks are just a bunch of links to other key areas of a site. However, if they contain lots of keywords that you want the site to rank for, they can help with you indexing for these keywords. Consider the following example of a link block used by Peter Kent.

Another expert tip involves adding a “What we do” block of text that can appear at the bottom of all web pages, which is kind of like an email signature file. For example, I use a WordPress plugin called Content Blocks. It is a place where you can add the same content to any web page by adding a content block that contains many of the overarching keywords that you want the site to rank for. The beauty of using a content block plugin is that you can create several tailored versions with different keywords included in the content, and with a simple drop-down selection, add them to individual web pages of your site. By simply adding a short-code to the content block, you can change the “What we do” text once and it is updated on all pages.
The following content block example is what I used on this page to add all my follow me on… links to the bottom of this blog post after my question to the reader.
In this way, each content block can contain text that hits on many keywords, perhaps a dozen or more, that you want your site to rank for. You can also include this paragraph in the footer area of your web pages as well.
How will you use your understanding of on-page visible elements to improve your SEO?
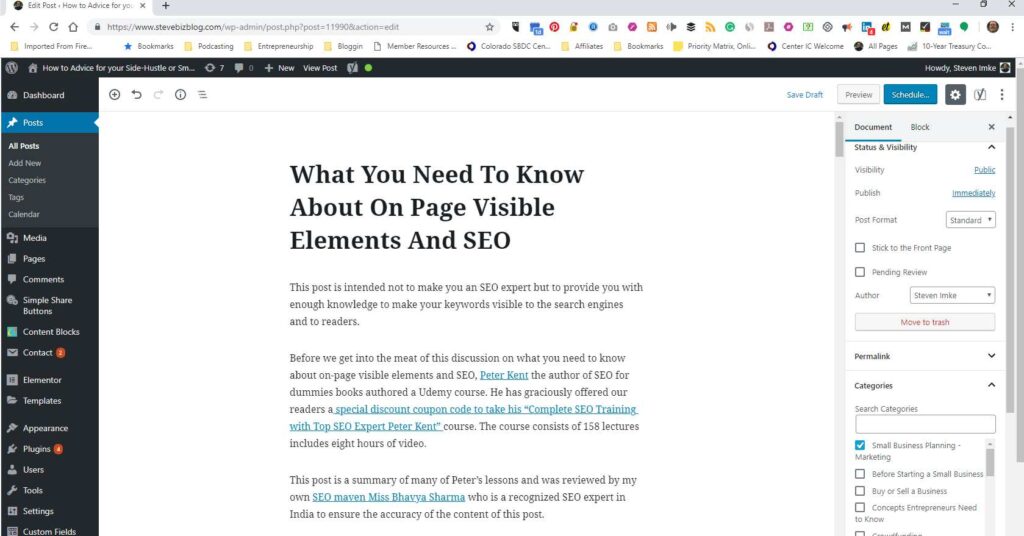
Peter Kent the author of SEO for dummies books authored a Udemy course. He has graciously offered our readers a special discount coupon code to take his “Complete SEO Training with Top SEO Expert Peter Kent” course. The course consists of 158 lectures includes eight hours of video.
This post is a summary of many of Peter’s lessons and was reviewed by my own SEO maven Miss Bhavya Sharma who is a recognized SEO expert in India to ensure the accuracy of the content of this post.
Related Post in SEO Series:
- Keywords-Everything You Wanted to Know But Were Afraid to Ask
- 20 Steps to Find Powerful Keywords Google will Rank High
- On-Page But Hidden SEO Techniques You Need To Understand
- What You Need To Know About On-Page Visible Elements And SEO
- What you Need to Know About Link Building
- What You Need to Know About a Backlinks and SEO
- How To Find The Best Performing Keywords And Rank Higher In SERP
- How Your SEO Actions Expose You As A Cheater Or A Star